Introduction
Did you ever wonder how platforms like Codeshare are built? Did you ever try to tackle the challenges of scaling a service like that while maintaining a good developer experience for yourself? When I decided to build Bytecrowds, I had to learn how to do all these. Doing rigorous research followed by the decision to use Yjs for providing text-sharing capabilities, it came time to choose a database. With so many options available on the market, I narrowed down the list using one essential keyword: simplicity
Why Upstash?
Even before discovering Upstash, I was interested in Redis® for its simple API. However, using it as a primary database comes with challenges like scaling(you might need this for caching too) and maintaining persistence. At the same time, before securing any sponsorship, you have to be very careful about budgeting an open-source software. Will you pay for the computing power even if it's not used at times? Can you handle a sudden traffic spike and be ready to spend hours working on infrastructure instead of working toward publishing new features, improving existing ones, or fixing some bugs? I, for one, wasn't. So I found Upstash.
The Upstash Redis offering matches 3 of my essential criteria: it's easy to use, easy to scale, and flexible. Combine that with low latency, out of the box REST sdk to use in serverless clients(a requirement for Bytecrowds too), global replication and a pay-as-you-go plan for the computing power, to name a few, and you will understand why I chose it for my project.
Using Redis® across the app
Let's find out how Redis® can be used as the main database of a project, fulfilling the needs of multiple services. To understand the context, here is a diagram of Bytecrowds's flow:
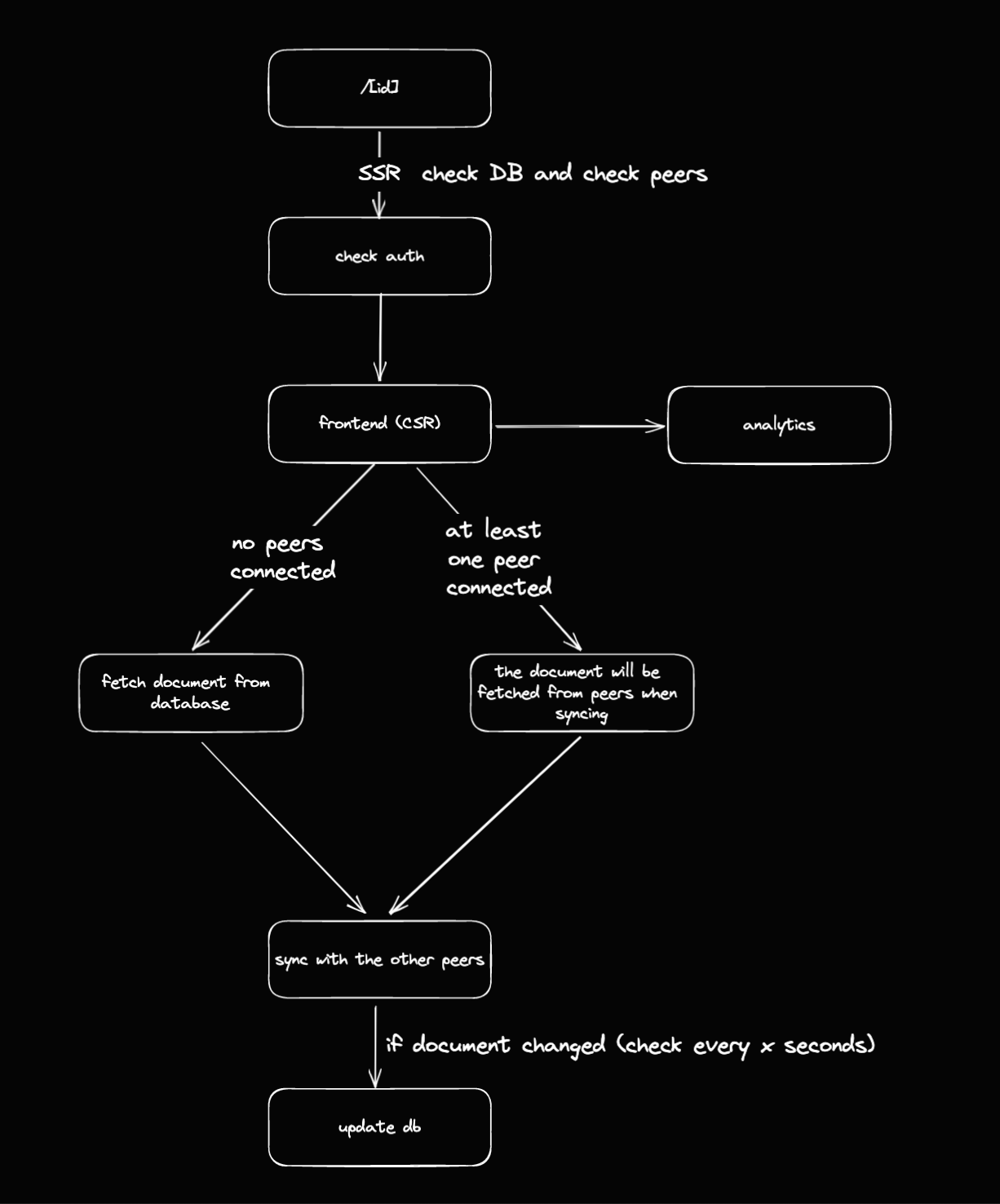
It uses Ably to sync text across clients and a custom analytics engine that collects data based on the request's IP address.
Main storage
A bytecrowd takes the form of a Redis® hash with the following properties:
{
text: string,
language: string,
authorizedEmails: undefined || string array
}We update the hash once one of its properties changes, with a delay of "x" seconds between updates. In production, this is currently set to 100 milliseconds.
Authentication and authorization
Authentication
As Bytecrowds uses Next.js, a solid choice for integrating GitHub OAuth was Auth.js. Fortunately, we could also leverage the Upstash adapter for storing sessions, allowing us to use Redis® all across our app.
Authorization
Bytecrowds handles authorization by creating, on demand, an authorizedEmails field that is immutable from the API once set. One of the things I like about Redis® is the multitude of functions available out of the box for routine operations that are also algorithmically designed to be efficient. To give an example, all we need to do to check if the authorizedEmails has already been set is to use the HEXISTS command, which has O(1) complexity.
Analytics
Bytecrowds uses an analytics system that handles two categories of data:
- a day's stats, which takes the form of a Redis® hash, named like
year month daywith the following properties:
{
countries: string array,
hits: integer,
pages: string array,
uniqueVisitors: integer,
addresses: string array,
continents: string array
}Where addresses is an array of SHA256-encrypted IP addresses used to determine the unique number of website visitors.
- 3 keys named
continents,countries, andpagesfor which Redis® sorted sets were used to store the data By storing every stat along with its count ("score", for the sorted set), we can easily query or sort them using commands like SORT or SORT_RO. Redis's simplicity shows again.
If you're curious about the code behind this, check https://github.com/Bytecrowds/analytics/blob/main/src/index.js
Note: In a more complex scenario, you'd probably apply some changes to this system, like storing the raw data before processing and using some sort of stream processing tool like Apache Kafka (Upstash can take care of this too, check the docs).
See it live
Want to see Bytecrowds in action? Go to https://www.bytecrowds.com, click on the "new bytecrowd" button and open the link in multiple tabs. When you start writing, you'll see that the code is replicated across all of the connected clients.
Ending
It's no secret that being the sole active maintainer of an open-source project is hard, but having the right tools and an auto-scaling infrastructure can be a great support that backs you up to continue working on awesome projects, without having to worry about traffic spikes. Already convinced to give Upstash Redis® a try? Sign up for a free account, no credit card is required.
To see the full code, check the GitHub repository. If you have any questions or feedback about this article, reach out to me at tudor.zgimbau@gmail.com.
